Human life is a work of muscles. Any conscious or unconscious activity is provided by their contraction or relaxation. These contractions or relaxations occur under the influence of nerve impulses passing through the nervous system from the spinal and brain. Here are some facts about these parts of our body:
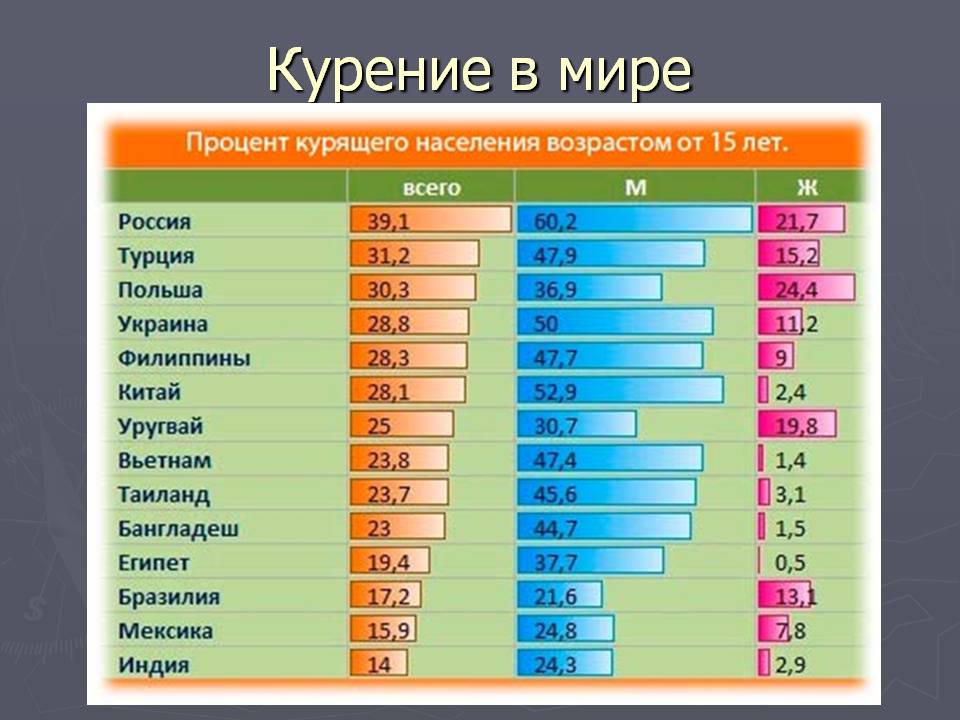
1. Scientists count a minimum of 640 muscles in the human body. By various estimates, there may be up to 850 of them. The differences are not because different people have different muscles. Medicine and anatomy are serious and old sciences, so their representatives simply must have theoretical disagreements.
2. It is believed that the resource of the average person’s heart muscle is designed by nature for 100 years of work (of course, continuous). The main enemies of the heart are a lack of glycogen and an excess of calcium.
3. One-quarter of human muscles (if you consider the total number) are in the head. And they start working and developing even in the intrauterine period of life.
4. When expressing negative emotions, 2.5 times more facial muscles are involved than when expressing positive ones. So crying is a better workout for facial muscles than laughter. Kisses occupy an intermediate position.
5. The tailor muscle, located in the front part of the thigh, is the longest in the human body. Due to its spiral shape, its length usually exceeds 40 cm. Sometimes the diaphragm is considered the longest muscle, but we breathe with a whole system of muscles, together forming the diaphragm.
6. The shortest muscles (their size is just over 1 mm) are located in the ears.
7. Strength training, in simplified terms, is gaining small tears in muscle fibers. Muscle mass and volume increase after a workout, during recovery, when amino acids and proteins «heal» the muscles, increasing the diameter of the fibers.
8. To increase muscle mass, serious efforts are needed. Muscles atrophy on their own — just look at astronauts returning from space flights. They often look exhausted from hard work, although they have not undergone any physical training — muscles degrade without loads.
9. Muscles also atrophy with age. In the second half of life, a person loses a few percent of muscle mass annually just due to age.
10. By mass, the muscles of an average person are approximately evenly distributed between the legs and the rest of the body.
11. The circular muscle of the eye, one of its functions being raising and lowering the eyelid, contracts faster than all others. It contracts very often, leading to the rapid formation of wrinkles around the eyes, which is discouraging for representatives of the fair sex.
12. The tongue is sometimes called the strongest muscle, but with all its strength, it consists of four muscles, the strength of which cannot be distinguished. Approximately the same picture with the chewing muscles: the effort produced is distributed among four muscles. Therefore, it is more correct to consider the calf muscle the strongest.
13. Even taking a single step, a person engages more than 200 muscles.
14. The specific weight of muscle tissues significantly exceeds the corresponding indicator of fat tissues. Therefore, a person engaged in sports is always heavier than a person far from sports with the same external dimensions. A little bonus: plump people who do not play sports find it easier to float on water.
15. Muscle contractions consume about half of all the energy generated by the body. Muscle mass burns after fat, so sports are effective for weight loss. On the other hand, serious physical exertion for a person with few fat reserves and inadequate nutrition quickly leads to exhaustion.
16. About 16% of people have a rudimentary muscle in their forearm called the long muscle. It remains in humans as a legacy from animals that released claws with its contraction. You can see the long muscle by bending your wrist toward the wrist. And the same rudimentary muscles, like the ear and pyramidal (pouch animals support their young with it) are present in everyone but not visible from the outside.
17. Sleep is a very important factor in muscle development, paradoxically. Muscles receive the maximum amount of blood during complete relaxation, that is, during sleep. All meditation practices, introspection, etc. are nothing more than an attempt to maximally relax the muscles to provide access to blood.
18. Many muscles in the body work without conscious control by the person. A classic example is the smooth muscles of the intestines. The processes of digestion take place in the internal organs on their own and sometimes lead to very unpleasant consequences.
19. Work schedules (in a 12-hour workday) ‘two out of three,’ i.e., two days off after a long workday, or ‘day — night — two days home’ appeared for a reason. Most muscle groups require two days for recovery.
20. The heel spur is a problem not with the bone, but with the muscles. It occurs with fasciitis — inflammation of the thin muscle sheath called the fascia. In its normal form, it prevents different muscles from contacting each other and the skin. The inflamed fascia transmits pressure directly to the muscle, which, due to unpleasant sensations, is similar to the effect on an open wound.